
- Healthcare
- Web Development
Healthcare Software Product Development Guide for 2024
The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital revolution unlike ever before. Fueled by a surge in data, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), and the ever-growing demand for patient-centric care, healthcare software adoption has skyrocketed in recent years. According to a source on** healthcare software market size**: the global healthcare IT market reached a value of USD 418.2 billion in 2023, and is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.5% to reach a staggering USD 760.5 billion by 2030. This explosive growth underscores the critical role software now plays in modern healthcare.
As we move through 2024, this trend is only expected to accelerate, creating a dynamic and exciting environment for healthcare software product development. This guide serves as a roadmap for navigating the current landscape and developing successful healthcare software products in 2024. We'll delve into key considerations, emerging trends, and best practices to equip you with the knowledge needed to create impactful solutions that benefit both healthcare professionals and patients.
The Role of Healthcare Software Products in Improving Patient Care

Healthcare software products are playing a transformative role in revolutionizing patient care. These innovative solutions offer a multitude of benefits that enhance the overall patient experience and contribute to better health outcomes. Here are some key areas where healthcare software shines:
-
Enhanced Communication and Engagement: Software solutions like patient portals and telehealth platforms facilitate seamless communication between patients and providers. This empowers patients to take a more active role in their health management, fostering better engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
-
Improved Data Management and Analytics: Healthcare software enables efficient collection, storage, and analysis of vast amounts of patient data. This data can be used to personalize treatment plans, identify potential health risks early on, and optimize healthcare resource allocation.
-
Increased Efficiency and Streamlined Workflows: From electronic health records (EHRs) to appointment scheduling software, various solutions streamline administrative tasks and workflows for healthcare professionals. This allows them to dedicate more time to patient care, leading to improved quality of care.
-
Diagnostic Support and Precision Medicine: Advanced software applications, powered by AI and machine learning, are revolutionizing diagnostics. These tools can analyze medical images, identify patterns in patient data, and assist healthcare professionals in making more accurate diagnoses and tailoring treatments to individual patients.
-
Remote Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management: Telehealth and remote monitoring solutions enable healthcare professionals to track patients' health remotely, particularly those with chronic conditions. This allows for early intervention in case of potential complications and improved overall management of chronic illnesses.
Tailored Solutions: Features of Custom Healthcare Software Products
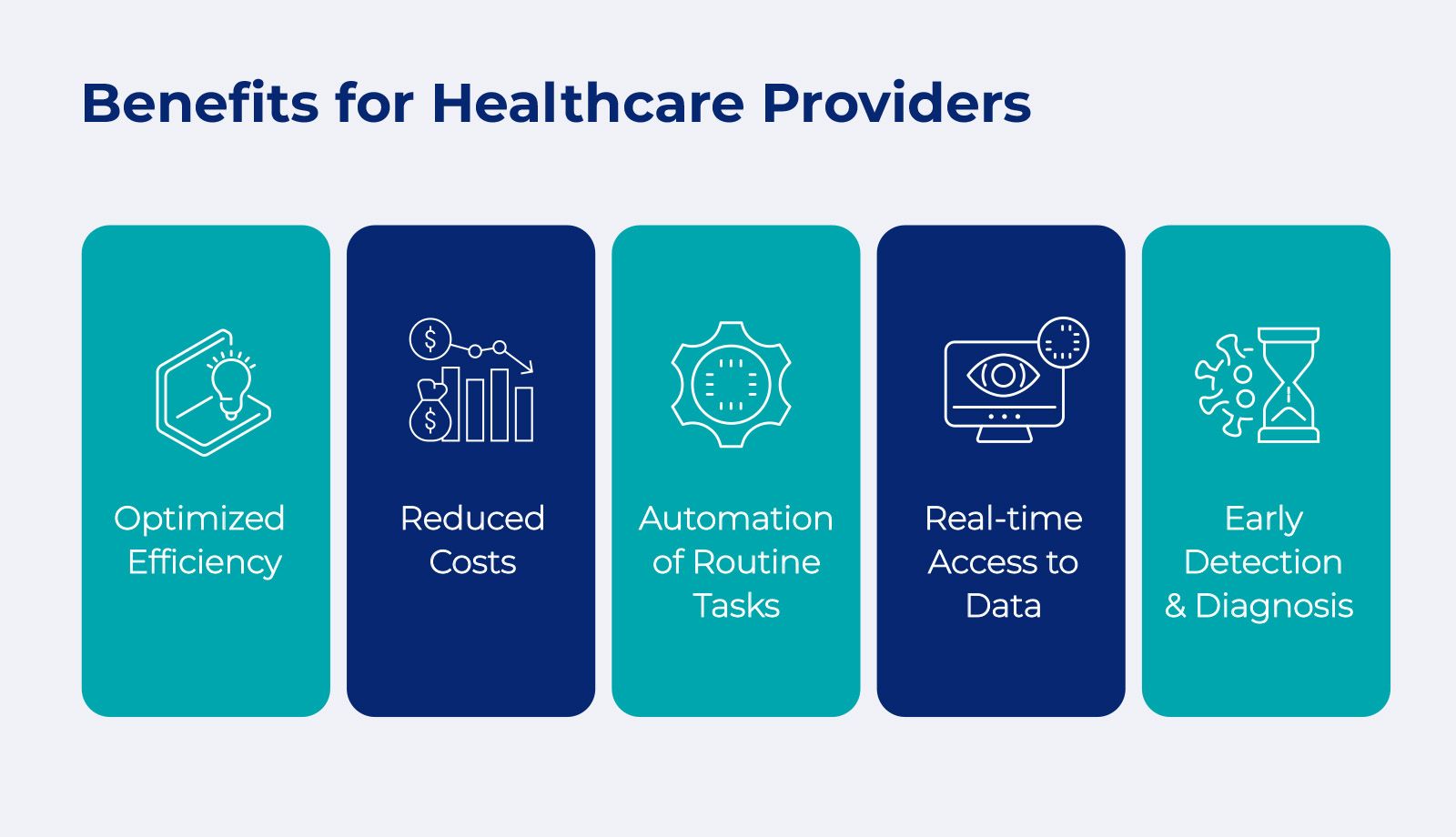
While off-the-shelf software offers a baseline level of functionality, the true power lies in custom healthcare software development. These bespoke solutions are meticulously crafted to address the specific needs and challenges faced by your unique healthcare organization. Here's a breakdown of key features that can be incorporated into your custom healthcare software product:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Management: A robust EHR system forms the backbone of any healthcare software solution. Custom development allows for seamless integration with existing systems and ensures your EHR caters to your specific data collection and management requirements.
- Telehealth and Virtual Care Features: Integrate functionalities for secure video conferencing, remote patient monitoring, and online appointment scheduling, empowering healthcare professionals to deliver care virtually and enhance patient accessibility.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): Leverage AI-powered CDSS tools to provide evidence-based recommendations during patient diagnosis and treatment planning. This can improve the accuracy and efficiency of clinical decision-making.
- Patient Engagement Tools: Build features like patient portals, medication reminders, and secure messaging functionalities to foster better patient-provider communication and encourage patient self-care management.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting: Customizable dashboards and reporting tools allow healthcare professionals to glean valuable insights from patient data. This data can be used to identify trends, optimize operations, and track progress towards quality improvement goals.
- Security and Compliance: Healthcare software handles sensitive patient data. Custom development allows for robust security protocols and ensures compliance with HIPAA regulations and other relevant data privacy standards.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing hospital information systems, labs, and pharmacies eliminates data silos and streamlines workflows. Scalability and Flexibility: Custom software can be designed to adapt and grow with your organization's needs. This ensures your software solution remains relevant and effective as your healthcare practice evolves.
Navigating the Landscape: Different Types of Healthcare Software
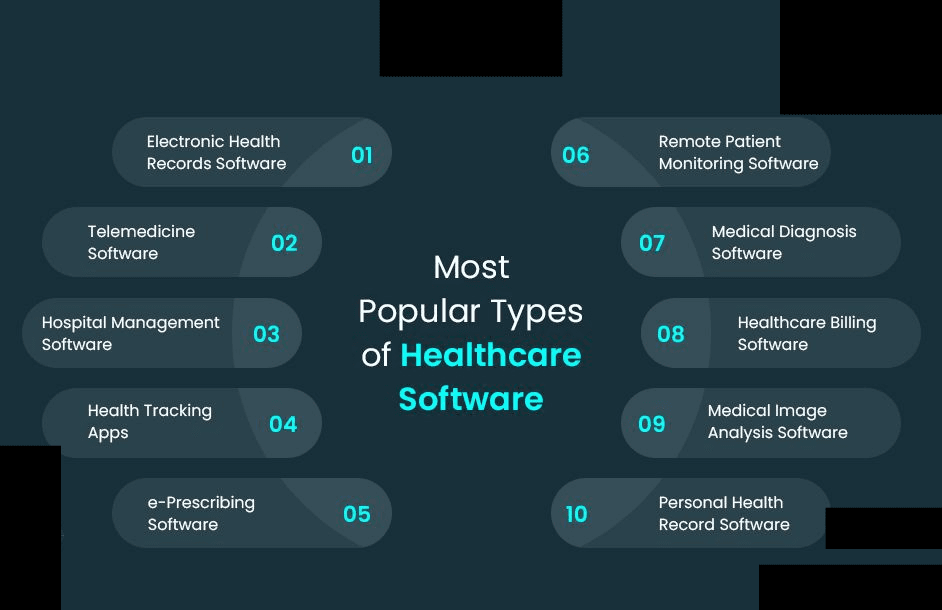
The healthcare software landscape is vast and encompasses a wide range of solutions designed to address diverse needs. Understanding these different types is crucial for determining the best fit for your organization. Here's an overview of some of the most common categories:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems: EHRs serve as the digital foundation for patient data management. They allow healthcare professionals to electronically document a patient's medical history, medications, allergies, and treatment plans. EHR systems can be standalone solutions or integrated with broader healthcare software suites.
- Practice Management Software (PMS): PMS solutions streamline administrative tasks within a healthcare practice. They typically handle functionalities like appointment scheduling, billing and coding, claims submission, and electronic communication with patients and insurance companies.
- Telehealth and Virtual Care Platforms: These solutions enable healthcare professionals to deliver care remotely through video conferencing, online consultations, and remote patient monitoring. This allows for greater patient accessibility and facilitates convenient care delivery.
- Hospital Management Systems (HMS): HMS are comprehensive software suites designed to manage various aspects of hospital operations. These systems typically encompass functionalities like patient registration, lab and radiology results management, pharmacy management, and resource scheduling.
- Medical Imaging Software: This software allows healthcare professionals to capture, view, analyze, and store medical images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Advanced functionalities include image manipulation tools, 3D reconstruction capabilities, and AI-powered analysis for faster and more accurate diagnoses.
- Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): LIMS solutions manage laboratory workflows, from sample collection and testing procedures to result generation and reporting. These systems automate tasks, ensure data integrity, and streamline lab operations.
- Pharmacy Management Software: These solutions assist pharmacists in managing medication inventory, dispensing prescriptions, and tracking patient medication adherence. Advanced functionalities may include integration with electronic health records and features for medication reconciliation.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): CDSS software utilizes AI and machine learning to provide healthcare professionals with real-time evidence-based recommendations during patient care. These tools can improve diagnostic accuracy, suggest appropriate treatment options, and help to reduce medication errors.
- Patient Engagement Tools: This category encompasses software solutions designed to promote better patient-provider communication and self-care management. Examples include patient portals, secure messaging functionalities, medication reminder apps, and online appointment scheduling tools.
- Healthcare Analytics Software: These solutions collect and analyze vast amounts of healthcare data to identify trends, optimize resource allocation, measure quality of care, and support data-driven decision making within healthcare organizations.
Step-by-Step Process of Healthcare Software Product Development
Developing successful healthcare software requires careful planning, meticulous execution, and a deep understanding of the healthcare industry's unique regulations and requirements. Here's a step-by-step process to guide you through the journey:
1. Identifying Needs and Defining Requirements:
The foundation of any successful software development project lies in a clear understanding of the problem you're trying to solve. This initial phase involves:
- Needs Assessment: Conduct thorough research to identify the specific challenges and opportunities within your healthcare organization. Gather input from various stakeholders, including healthcare professionals, patients, and administrative staff.
- Competitive Analysis: Analyze existing healthcare software solutions in the market to understand their functionalities, strengths, and weaknesses. This will help identify potential gaps you can address with your custom product.
- Feature Prioritization: Based on the needs assessment and competitive analysis, prioritize the features that will deliver the most significant value to your organization and patients.
2. Planning and Design:
With a clear understanding of your requirements, it's time to translate them into a concrete plan and design:
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Selection: Choose a suitable SDLC methodology (e.g., Agile, Waterfall) that aligns with your project scope and team structure. An Agile approach is often preferred in healthcare software development for its adaptability and iterative development cycles.
- System Architecture Design: Define the software's overall architecture, including hardware, software components, and data flow. Consider factors like scalability, security, and compliance with healthcare data privacy regulations.
- User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) Design: Design user-friendly interfaces that cater to the specific needs of healthcare professionals (clinicians, administrators) and patients. Prioritize intuitive navigation, clear information hierarchy, and data visualization to ensure a seamless user experience.
3. Development and Testing:
Following a well-defined plan, development begins:
- Software Development: Your development team will use appropriate programming languages and frameworks to bring your software to life. Security best practices and adherence to HIPAA regulations are paramount throughout the development process.
- Testing and Quality Assurance (QA): Rigorous testing is crucial to ensure the software functions flawlessly, delivers accurate results, and meets all compliance requirements. Testing should encompass unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT).
4. Deployment and Maintenance
Once the software is thoroughly tested and validated, it's time to deploy it:
- Implementation and Training: Deploy the software within your healthcare organization and provide comprehensive training to healthcare professionals and staff on how to effectively use the new system.
- Ongoing Support and Maintenance: To ensure continued optimal performance and address any potential issues, provide ongoing support and maintenance services. This may include bug fixes, feature updates, and security patches.
5. Continuous Improvement:
In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, successful software evolves alongside it:
- Feedback and Monitoring: Continuously gather feedback from users and monitor the software's performance to identify areas for improvement.
- New Feature Development: Based on user feedback and industry trends, consider developing new features and functionalities to enhance the software's capabilities and user experience.
Ensuring Safety and Regulatory Requirements of Building Healthcare Software Products
Developing healthcare software comes with a significant responsibility – ensuring the safety and well-being of patients. Regulatory compliance is paramount, as these solutions handle sensitive patient data and directly impact healthcare delivery. Here's how to prioritize safety and navigate regulatory requirements during the development process:
1. Security Best Practices:
- Data Encryption: Implement robust data encryption protocols at rest and in transit to safeguard sensitive patient information.
- Access Control: Enforce strict access controls to ensure only authorized personnel can access patient data based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
2. HIPAA Compliance:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) regulations govern the privacy and security of protected health information (PHI) in the United States. Adherence to HIPAA is essential for any healthcare software product that handles patient data.
- HIPAA Security Rule: This rule mandates specific administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect electronic PHI (ePHI). Ensure your software development process adheres to these safeguards, such as conducting risk assessments, implementing security measures, and maintaining audit trails.
3. Additional Regulatory Considerations:
- FDA Regulations: Depending on the intended use of your healthcare software, it may be classified as a medical device by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This classification determines the level of regulatory scrutiny required for pre-market approval.
- International Standards: If your software is intended for use in other countries, be mindful of their specific healthcare data privacy regulations and adapt your development process accordingly.
4. Focus on Patient Safety:
- Rigorous Testing: Implement a comprehensive testing strategy that goes beyond functionality to ensure patient safety. This includes testing for potential errors, data integrity, and system failures that could compromise patient care.
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Design fail-safe mechanisms to minimize the risk of errors and ensure the software behaves predictably in case of unexpected system issues.
- User Training: Provide proper training to healthcare professionals on how to utilize the software safely and effectively to avoid potential misuse or misinterpretations of data.
Use-Cases of Healthcare Software Product Development
The applications of healthcare software development are vast and constantly evolving. Here are some compelling use cases that showcase the transformative potential of these solutions:
- Improved Patient Engagement: Custom patient portals empower patients to take a more active role in their health management. These portals allow patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, communicate with healthcare providers securely, and manage medications.
- Telehealth and Remote Monitoring: Telehealth platforms enable virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and chronic disease management. This allows for increased patient accessibility, improved care delivery in rural areas, and timely intervention for potential health concerns.
- Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS): AI-powered CDSS tools support healthcare professionals by providing real-time evidence-based recommendations during diagnoses and treatment planning. This can potentially improve diagnostic accuracy, reduce medication errors, and optimize treatment regimens.
- Precision Medicine and Personalized Care: Advanced healthcare software facilitates the analysis of vast amounts of patient data, including genetic information. This paves the way for personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatments to individual patient needs and genetic profiles.
- Streamlined Hospital Operations: Hospital Management Systems (HMS) integrate various functionalities like patient registration, lab results management, pharmacy management, and resource scheduling. This streamlines workflows, improves efficiency, and allows healthcare professionals to dedicate more time to patient care.
- Enhanced Medical Research: Healthcare software solutions facilitate data collection, analysis, and collaboration in medical research. This can lead to faster breakthroughs in drug discovery, development of personalized treatment options, and improved preventative care strategies.
Conclusion: Empowering Healthcare with Innovation
The healthcare software landscape is brimming with potential to revolutionize patient care, optimize operations, and drive positive outcomes for healthcare providers and patients alike. By understanding the development process, prioritizing safety and compliance, and focusing on relevant use cases, you can leverage the power of healthcare software to create innovative solutions that make a real difference in the healthcare industry.
Codenomad, a leading healthcare software development company, is here to partner with you on your journey. Our team of experienced developers and healthcare specialists understands the unique challenges and opportunities within the healthcare sector. We leverage cutting-edge technologies and prioritize patient safety and regulatory compliance to craft custom healthcare software solutions that empower your organization and deliver exceptional value.
Contact Codenomad today to discuss your specific needs and explore how custom healthcare software development can transform your organization and elevate the quality of care you provide.
Search
Never Miss A Post!
Sign up for free and be the first to get notified about updates.
Stay In Touch
Sign up for free and be the first to get notified about updates.

